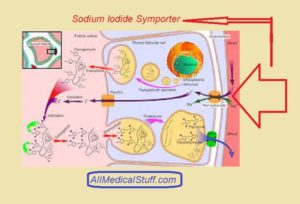
Sodium-iodide symporter, also called sodium iodide pump or iodide pump is present in thyroid gland and helps in the active transport of iodide to follicular cells of thyroid.
What is Sodium Iodide Symporter:
As mentioned above, it is an active transporter or pump that uses electrochemical gradient of sodium. As sodium is less inside than outside, it is transported inside and an iodide is also bounded to this channel. Iodide is this case is traveling against concentration gradient. Because iodide is 20-50 times more in thryoid follicular cells as compared to outside. Therefore this channel is also called pump.
Other Names:
NIS (sodium iodide symporter) is also called sodium iodide pump, iodide pump and sodium iodide cotransporter. Therfore if you read these names somewhere instead of symporter, don’t confuse yourself with it.
Location:
Sodium iodide cotransporter is located in thyroid gland in general. And specifically, it is located in the basolateral membrane of follicular cells of thyroid gland.
As you know, there are two types of cells in thyroid gland. One is called follicular cells and the other is called C cells. C cells are concerned with the production of calcium regulatory hormone called calcitonin and it has nothing to do with thyroid pump.
Therefore, sodium iodide symporter is only present in the baso lateral membrane of follicular cells of thyroid.
Functions of Sodium Iodide Symporter:
The main function/role of this pump is to transport iodide inside the cells of thyroid gland (follicular cells) against the concentration. Therefore it is involved in the 1st step synthesis of thyroid hormones that is thyroxine and triiodothyronine. You can learn in detail about thyroid hormones synthesis here.
Sodium Iodide Cotransporter Defect/Pathology:
There is a rare congenital defect of this pump and it has known to be having a role in thyroid cancer. Use of radioactive iodide has proven to be useful in its destruction.
Recommended: Learn the differences between triiodothyronin and thyroxine.
Leave a Reply