Urea is the waste end product of amino acids or protein metabolism. Or you can also say urea is the metabolic end product of amino acids and proteins. As urea is the waste product and it is eliminated from the body by kidneys. So, what would happens if the kidneys get damaged and doesn’t eliminate urea? It would accumulate in the body. Therefore, blood urea concentration can be a good indicator of many diseases. That’s why estimation of blood urea is one of the important test thought in every medical school in biochemistry practical.
So it is very essential for a medical student to have some information about blood urea estimation and its methods. Here below, you would find everything that is important for a medical student regarding urea. And yes it would also help to complete you practical notebook as well.
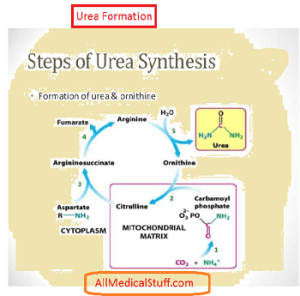
Urea Synthesis:
Urea is synthesized in Liver in five steps. The first two step occur in mitochondria while the other three in cytosol. From the image below, you can learn all the five steps:
Blood Urea estimation can be done using any two methods given below. You can use any of them but the more advanced one is enzymatic method that is used widely and it has more accurate results.
Estimation Of Blood Urea By DAM Method:
DAM method stands for Di Acetyl Monoxime method. This method is quite similar to the other method but the difference is that urease enzyme is not used in this method.
DAM Reagents:
Reagents for this method are the following:
- Di acetly monoxime solution (R1)
- Ferric ammonium sulphate or ferric alum (R2)
- Standard Solution of Urea (30mg/dl)
Procedure:
Here is the step by step procedure of DAM Method:
- First of prepare protein free filtrate. Learn how to prepare protein free filtrate here.
- Then Take 3 test tubes. Label them unknown, standard and blank respectively.
- Then add 0.5 ml of PFF in unknown. O.5 ml of standard solution in standard and 0.5 ml of distilled water in blank.
- Dilute the contents of all the test tubes by adding 1.5 ml of dist water.
- Add 2ml of reagent R1 (DAM solution) to all the test tubes.
- Keep all the test tubes in boiling water bath for 10 minutes.
- Then add 2ml of Reagent R2 to all the test tubes.
- Then keep all the test tubes at room temperature for 10 minutes.
- Find optical density using photo colorometer at 540 nm. Use path length= 1cm.
- Find concentration of unknown using Beer-Lambert Law.
Estimation Of Blood Urea By Berthelot Method:
This is the modern method for blood urea estimation and is more accurate as compared to Di acetyl monoxime method. In this method we use urease enzyme to convert urea into ammonia and CO2. More detail is given in principle blow.
Principle Of Berthelot Method:
As mentioned above the principle of this test is to convert urea enzymatically to NH3 and CO2 using urease enzyme. Ammonia is then converted dicaroboxy endo phenol which is a blue colored compound. The intensity of this blue colored compound is directly proportional to amount of urea in blood. As the more urea in blood, the more would be dicarboxy endo phenol formed and the more intense would be the color.
Berthelot Reaction:
Berthelot reaction is the one mentioned above in principle. Look at the picture above in principle.
Berthelot Reagent:
It is an alkaline solution of hypochlorite and phenol. This is used to convert ammonia into a blue compound dicarboxy endo phenol. The intensity of this blue colored compound can then give the amount of ammonia present in a solution using photo colorometer or spectro photometer.
This can be used for ammonia estimation as well as urea estimation (only in enzymatic method and not in DAM method). As in urea estimation by urease enzyme NH3 is formed which is the basis of this method.
Reagents:
Three reagents are used in this method. They are following:
R1:
- Buffer phosphate 120 m mol/L
- Sodium Salicylate 60 m mol/L
- Na nitroproside 5 m mol/L
- EDTA 1 m mol/L
- Urease enzyme 5 KU/L
R2:
- Phosphate Buffer 120 m mol/L
- NaOH 400 m mol/L
- Sodium hypochlorite 10 m mol/L
R3:
Standard solution of urea= 80mg/dl
Procedure:
Procedure of this experiment/test is very much similar like other quantitative laboratory tests. Here are all the step by step process:
- Take 3 test tubes. Label them as unknown, standard and blank.
- Then add 0.01 ml of serum in the test tube labelled unknown. 0.01 ml of standard solution in test tube labelled standard and 0.01 ml of distilled water in blank.
- Then add 1ml of Reagent R1 in all teh test tubes.
- Add 1ml of Reagent R2 in all the test tubes.
- Keep all the test tubes at room temperature for 10 minutes.
- Find absorbance at 578 nm using photo colorometer.
- Find concentration of unknown using Beer-Lambert law.
Precautions:
Take care of the following things:
- Use the exact amount of reagents as mentioned in the procedure above.
- Label all the 3 test tubes so that you don’t get confused.
- Find absorbance only at the wavelength mentioned above.
- Use protein free filtrate in DAM method.
Results:
By finding the absorbance of unknown solution, you can easily calculate the amount of urea in blood using formula.
Normal Value of Blood Urea:
20-40 mg/dl is a normal range of blood urea level.
Increased Urea in Blood OR Uremia:
If more then normal urea is found in blood i.e more then 40 mg/dl then this condition is said to be Uremia. There could be three causes of uremia. They are following:
Pre Renal:
Pre-renal causes could be:
- Salt and water depletion i.e dehydration.
- Diarrhea
- Hemorrhage
- Sock after burns
- Diabetic coma
- Some major surgery
- Leukemia etc
Renal Causes:
Renal causes includes:
- Acute glomerulonephritis
- Mercury poisoning
- Pyelonephritis etc
Post renal Causes:
They are following:
- Enlarged prostate
- Bladder neoplasm
- Renal Stones etc
Final Words:
So, this was all about urea and its methods of estimating its concentration in blood. If you have any queries or want to contribute something to this post, kindly use the comment form below.

Leave a Reply