The curve, that explains a progressive increase in the percentage of hemoglobin bound with oxygen as blood partial pressure of oxygen increases, is called oxygen hemoglobin dissociation curve.And it is called the percent saturation of hemoglobin.
Oxygen is carried in the blood, in dissolved form and in combined form.Majority of it is carried in combined form with with hemoglobin.
When partial pressure of oxygen is more in blood, more oxygen combines with hemoglobin but when, the partial pressure of oxygen is less in blood, i.e in tissues, the oxygen molecule detaches from hemoglobin molecule.
Each hemoglobin molecule can combine with four oxygen molecules.The amount of oxygen combined with hemoglobin is called saturation of oxygen.
The oxygen hemoglobin dissociation curve is described by the following formula:
S(t) = 1/1+e-t
Factors effecting standard oxygen hemoglobin dissociation curve:
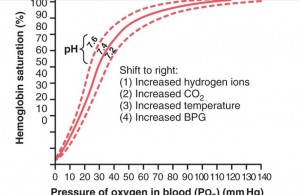
There are some factors that affect the standard dissociation curve.These factors shift or reshape the dissociation curve.A rightward shift indicated that hemoglobin has decreased affinity for oxygen.But makes it easy for oxygen to detach from hemoglobin.
The leftward shift indicates that the hemoglobin has increased affinity for oxygen.
Rightward shift of oxygen hemoglobin curve:
The rightward shift of oxygen hemoglobin curve indicated decreased hemoglobin affinity for oxygen.Thus less oxygen combines with hemoglobin.There are some of the reasons that effect rightward shift.
pH:
Increase in pH increases oxygen affinity for hemoglobin, while decrease in pH causes the rightward shift of oxygen hemoglobin curve.Thats the reason that oxygen detaches form blood at tissue level where pH is less due to the presence of more carbon dioxide.
Carbon dioxide:
Carbon dioxide increased concentration causes the rightward shift of oxygen hemoglobin dissociation curve.There are two reasons for this shift:
- Carbon dioxide accumulation in blood causes carbamino compounds to be generated through chemical interactions which bind to hemoglobin forming carbaminohemoglobin.
- It decrease pH of the blood, that decreases oxygen saturation.
2.3-DPG:
2,3-Diphosphoglycerate is an organophosphate, which is created in erythrocyte during glycolysis.In the presence of 2.3-DPG, the curve shift to the right causes low hemoglobin affinity for oxygen.
Temperature:
Increases in temperature weaken and denature the bond between oxygen and hemoglobin and shift the oxygen hemoglobin dissociation curve to the right.
Leftward shift:
The leftward shift of oxygen hemoglobin curve indicates greater affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen.here are some of the factors that causes leftward shift of the curve.
pH:
Increase in pH causes the leftward shift of oxygen hemoglobin curve.
CO2:
Decreaed carbon dioxide concentration causes the leftward shift of curve.This is due to:
- Decreased carbaminohemoglobin.
- pH is increases in absence of carbon dioxide.
2,3-DPG:
In the absence of 2,3-DPG the oxygen hemoglobin curve shift to left.
Temperature:
Decrease in temperature strengthen the bond between oxygen and hemoglobin and shift the oxygen hemoglobin curve to left.
Fetal hemoglobin:
Fetal hemoglobin is present in fetus and structurally different form normal adult hemoglobin Hb-A.Therefore, it has greater affinity for oxygen than Hb-A due to the presence of two gamma chains instead of beta chains.It causes the leftward shift of oxygen hemoglobin dissociation curve.
Impressive work. Keep it up..