Foramena of skull are opening in the skeleton of human skull through which various structures passes. These structures include arteries, veins, nerves, muscles etc.
As we are concerned with the foramena of skull, there are many foramen in skull but here we would mention some of the important one. We would also be list the sturctures that passes via them. In order to help you learn these foramena and their contents , we would be adding some mnemonics that would help you learn these skull foramens.
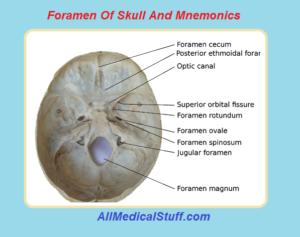
List of Foramena of Skull:
Before going into detail of each of the foramen of skull, first have a look at the names of these foramen and learn their names. After that you would be able to learn the structures that passes through them. Because without knowing these foramen, it would not be possible to learn the structures that passes through them.
- Foramen Magnum.
- Foramen Rotundum.
- Foramen Ovale
- Foramen Spinosum.
- Foramen Lacerum.
- Stylomastoid Foramen.
- Zygomaticotemporal Foramen.
- Inferior Orbital Fissure.
- Superior Orbital Fissure.
- Supra Orbital Foramen.
- Incisive canal.
- Greater palatine foramen.
- Lesser palatine foramen.
- Foramen Cecum.
- Mastoid Foramen.
- Mental Foramen.
- Mendibular foramen.
- Parietal Foramen.
Foramen of Skull Mnemonic With Structures:
Now we will discuss all the above mentioned foramen of skull with the names of structures that pass through them. And also mnemonics for them.
1. Foramen Magnum Contents:
The most important structure that passes via foramen magnum is medulla oblongata which continues as spinal cord after it passes through foramen magnum.
Other structures include vertebral arteries, ascending parts of accessory spinal nerves, membrana tectora and apical ligament of dens.
Foramen Magnum mnemonics:
Mnemonics for foramen magnum is MAVer.
In this mnemonic, M is for medulla oblongata, A is for ascending spinal nerves and Ver is for vertebral artery.
2. Foramen Rotundum Contents:
Maxillary nerve which is the second branch of fifth cranial nerve, called trigeminal nerve passes through this foramen rotundum.
3. Foramen Ovale Contents:
Five structures passes through this foramen. They are:
- Accessory meningeal nerve
- Lesser petrosal nerve
- Mandibular Nerve which is the third branch of trigeminal nerve.
- Anterior trunk of middle meningeal artery occasionally.
- Emissary vein
Foramen Ovale Mnemonics:
The mnemonics for foramen Ovale is MALE.
M is for Mandibular Nerve, A is for accessory meningeal nerve, L is for lesser petrosal nerve and E is for Emissary vein.
4. Foramen Spinosum Contents:
Three structures pass via foramen spinosum. They are: Nervous spinosum, Emissary vein, and Middle menengial artery and vein.
Foramen Spinosum Mnemonic:
To learn the content of foramen spinosum, you just have to keep in mind MEN. In which M is for Middle menegial artery and vein. E is for emissary vein and N for nervous spinosum.
5. Foramen Lacerum Contents:
It is a triangular foramen in the base of skull via which passes:
- Emissary vein.
- Internal Carotid Artery.
- Meningeal branch of Ascending pharyngeal artery.
- Greater petrosal nerve
Mnemonics For Foramen Lacerum:
To learn the content of this foramen, you have to keep in mind MEIG. Here is how you learn these structures from MEIG:
- M is for Meningeal branch of ascending pharyngeal artery.
- E is for Emissary vein.
- I is for internal caroid artery.
- And G is for greater petrosal nerve.
6. Stylomastoid Foramen:
Via it passes facial nerve which is the 7th cranial nerve. It also contains stylomastoid branch of posterior auricular nerve.
7. Zygomaticotemporal Foramen:
The nerve that passes via this foramen has the name of this foramen so it is quite easy to remember. The name of that nerve is zygomaticotemporal nerve.
8. Inferior Orbital Fissure:
It is the fissure that separates the floor of orbit from lateral wall and transmit few structures. The structures that it transmit are: ophthalmic vein and other infraorbital vessels, maxillary nerve (zygomatic branch) and the ascending branches of the pterygopalatine Ganglion.
9. Superior Orbital Fissure:
It is also a grove in orbit of the eye and is located between the greater and lesser wings of spheniod bone. Though it passes:
- Abducence nerve which is sixth cranial nerve.
- Ophthalmic vein (both superior and inferior divisions).
- Occulomoter nerver
- Trochlear nerve.
- Ophthalmic branch of trigeminal nerve.
- Sympathetic Fibres
10. Supra Orbital Foramen:
As the name suggest, this foramen is located above orbit. And it provides a path for transmission of supra orbital nerve and vessels i.s supra orbital artery and supra orbital vein.
11. Incisive canal:
The Greater palatine artery and nasopalatine nerve passes via this canal.
12. Greater palatine foramen:
Via the two vessels passes that has the same name as this foramen i.e greater palatine artery and vein. And also anterior palatine nerve passes via it.
13. Lesser palatine foramen:
Like the greater palatine foramen, via this also passes lesser palatine artery and vein and middle palatine nerve and posterior palatine nerve.
14. Foramen Cecum:
The only structure which passes via foramen cecum is emissary vein to superior saggital sinus which has clinical importance in transmission of infections from face to sinuses.
15. Mastoid Foramen:
This foramen is located in the posterior part of temporal bone. It transmits two structures that are:
- Emissory Vein to Sigmoid Sinus.
- Occipital Artery (meningeal branch)
16. Mental Foramen:
This foramen is located in the anterior surface of mandible and it transmits mental vessels and nerve.
17. Mendibular Foramen:
Mandibular foramen is presents in the ramus of mandible and transmits Inferior alveolar artery, vein and nerve.
18. Parietal Foramen:
It transmits parietal emissary vein from the superior sagittal sinus.
Makes easy for anatomy students to learn and understand the structural design of the human body.
thanks…started this site for the same purpose.