13 Clotting Factors:
There are main 13 clotting factors that help in the clotting of the blood. This process is also called coagulation. In this process blood changes from liquid to a gel like substance which is called clot. This is a protective mechanism which keeps the blood from loss after injury.
Clotting involves various steps and various pathways. There are main 13 factors but there are some other related substances that also help in clotting and are discussed below:
Absence of any of these factors results in various diseases, which are listed below in clotting factors table.
Clotting Factors Definition:
Clotting factor may be defined as ” the substance or group of substances that help in clot formation (coagulation) is called clotting factor.
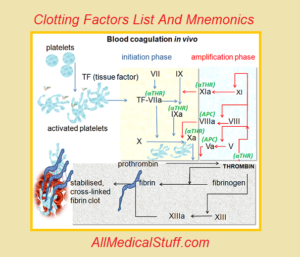
Clot formation/ coagulation is not a one step process. There are two different pathways i.e intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of coagulation. All of these factors are involved in different steps of clot formation. And missing of any of these factor causes various clotting diseases such hemophilia.
In order to learn about the diseases and the steps in which each of these factors work, you should read detail below or look at the table.
Clotting Factors Table:
| Sr No | Factor | Alternate Name | Function | Disorder |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Factor I | Fibrinogen | Form Fibrin | Congenital Afibrogenmia And Familial Renal Amyloidosis |
| 2 | Factor II | Prothrombin | Transformed into Thrombin which then activates factor I, V, VII, VIII, XI, XIII, Protein C and platelets | Thrombophilia |
| 3 | Factor III | Tissue Factor | Co factor of VIIa | |
| 4 | Factor IV | Calcium | Bind Coagulation Factors to phospholipids | No major effects |
| 5 | Factor V | Proaccelerin | Forms Prothrombinase with factor 10 | Activated protein C resistance |
| 6 | Factor VI | Accelerin | ||
| 7 | Factor VII | Stable Factor OR Proconvertin | Activates Factor IX & X | congenital proconvertin deficiency |
| 8 | Factor VIII | Anti Hemophilic Factor A | Forms Tenase Complex With Factor 9 | Haemophilia A |
| 9 | Factor IX | Antihemophilic factor B OR Christmas factor | Forms Tenase complex with factor 8 And Activates Factor 10 | Haemophilia B |
| 10 | Factor X | Stuart Prower Factor | Forms Prothrombinase complex with factor V and converts Prothrombin to thrombin | Congenital Factor 10 Deficiency |
| 11 | Factor XI | Plasma Thromboplastin Antecedent | Activates Factor 9 | Haemophilia C |
| 12 | Factor XII | Hageman factor) | Activates factor XI, VII and prekallikrein | Hereditary Angioedema type III |
| 13 | Factor XIII | Fibrin Stabilizing Factor | Congenital Factor 13 deficiency | |
| 14 | vWF | Von Willebrand factor | Binds to Factor 8 And Mediates platelet adhesion | Von Willebrand disease |
| 15 | Fletcher factor | Prekallikrein | Activates XII and prekallikrein; cleaves HMWK | Prekallikrein deficiency Or Fletcher Factor Deficiency |
| 16 | HMWK | High Molecular weight Kininogen | Supports reciprocal activation of XII, XI, and prekallikrein | Kininogen deficiency |
| 17 | Fibronectin | Mediates cell adhesion | Gomerulopathy with fibronectin deposits | |
| 18 | Antithrombin III | Inhibits IIa, Xa, and other proteases | Antithrombin III deficiency | |
| 19 | Protein C | Inactivates Va and VIIIa | Protein C Deficiency | |
| 20 | Protein S | Cofactor for activated protein C | Protein S deficiency | |
| 21 | Protein Z | Mediates thrombin adhesion to phospholipids and stimulates degradation of factor X by ZPI | Protein Z deficiency | |
| 22 | Plasminogen | Converts to plasmin, lyses fibrin and other proteins | Plasminogen deficiency | |
| 23 | Alpha 2 Antiplasmin | Inhibits plasmin | Antiplasmin deficiency | |
| 24 | tPA | Tissue plasminogen activator | Activates plasminogen | Thrombophilia |
| 25 | Urokinase | Activates plasminogen | Quebec platelet disorder | |
| 26 | Cancer procoagulant | Pathological factor X activation | Thrombophilia | |
| 27 | PAI1 | Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor 1 | Inactivates tPA & urokinase | Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 deficiency |
| 28 | PAI2 | Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor 2 | Inactivates tPA & urokinase |
Clotting Factors List:
- Clotting factor 1: Fibrinogen
- Clotting factor 2: Prothrombin
- Clotting factor 3: Tissue Factor Or Tissue Thromboplastin
- Clotting factor 4: Calcuim
- Clotting factor 5: Proaccelerain
- Clotting factor 6: Accelerin or Factor 5a
- Clotting factor 7: Stable Factor OR Proconvertin
- Clotting factor 8: Antihemophilic Factor A
- Clotting factor 9: Christmass Factor OR Antihemophilic Factor B
- Clotting factor 10: Staurt Prower Factor
- Clotting factor 11: Plasma Thromboplastin Antecedent
- Clotting factor 12: Hageman Factor
- Clotting factor 13: Fibrin Stabilizing Factor
- vWF Or Von Willebrand factor
- Prekallikrein (Fletcher factor)
- High Molecular weight Kininogen or HMWK (Fitzgerald factor)
- Fibronectin
- Antithrombin III
- Protein C
- Protein S
- Protein Z
- Plasminogen
- Alpha 2 antiplasmin
- Tissue plasminogen activator or tPA
- Urokinase
- Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor 1 (PAI1)
- Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor 2 Or PAI2
- Cancer procoagulant
13 Clotting Factors Mnemonics:
There are many mnemoincs for learning 13 clotting factors. I have collected some of the best and shared below:
Fresher’s Party Tonight, Come Let’s Sing And Call Seniors, Please Have Fun
Foolish People Try Climbing Long Slopes After Christmas Some People Have Fallen
Clotting Factors ppt:
If you want a power point presentation to learn each factor in detail or to deliver a presentation, you can do so by downloading a clotting factor ppt below:
Clotting Factors pdf:
We have a pdf guide in which all the clotting factors are discussed in detail. You can download it from here.
Thanks so much for sharing your knowledge with us. May God continue to bless you. Pls,can you be my tutor? I’m in school of nursing in Nigeria. All the subjects seems to be too bulking for especially anatomy, foundation of nursing, primary health care, computer etc. I will be expecting your positive reply. Once again, thank you and God bless you
sorry i don’t have time. but i can write on topics for you on this blog.