What is a joint:
The junction between two or more bones or cartilage is called a joint.Joints keeps the bones attached to one another and permits them to move.Some of them don’t permit movement,while other permit slight movement and some permit freely movement.
Due to the degree of movability joints are classified into three classes.But they are also classified according to their shape,function,location,and number of bones.All of these are discussed one by one:
1:Classification of joint on the basis of movability or Functional classification of joints:-
Joints are classified into three classes on the basis of movabiliy.These three classes are:immovable joints,partially movable joints and freely movable joints.
Immovable joints:
These joints doesn’t permit movement and the bones are articulated by tough fibrous tissue.Examples of such bones are sutural bones etc.They are also called Synarthroses.
Partially movable joints:
These joints show slight movement.A pad of cartilage is present between the two articular bones which sometimes act as shock absorber like inter-vertebral disk between vertebrae.In these joints the bones and cartilage are hold by fibrous ligaments.They are also called Amphiarthroses.
Freely movable joints or sinovial joints:
These joints show free moveabliliy but sometimes the movement is restricted due the shape of articulating surfaces and ligaments which hold these bones together.
These joints have a fluid cavity called sinovial cavity which contains a lubricating fluid called sinovial fluid.This fluid is secreted by sinovial membrane.These joints are also called Diarthroses.
The movements which are possible at sinovial joints are:
Flection: When the angle between the two bones is decreased.
Extension:When the angle between two bones is increases.
Abduction:Moving the part away from the mid-line.
Adduciton:Moving the part towards the mid-line.
Rotation:Turning the bone upon its axis.
Circumduction:Moving the extremity of the part round in a circle so that the whole part inscribes a cone.
Gliding:when one bone slides on the other.
2:Classification of joints according to the number of articulation bones:-
Simple Joint:
A joint in which two bones articulate eg.interphalangeal joint.
Compound joint:
When more than two bones articulate within one capsule like elbow joint.
Complex joint:
When interarticualar disc divide the joint cavity like acromioclavicular and sternoclavicular joint.
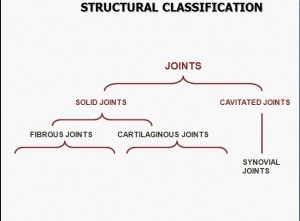
3:Structural classification of joints:
According to structure joints are classified into two main branches that are:
A:solid joints:-
These are further divided into fibrous joints and cartilaginous joints.
B:Cavitated joints:-
These includes sinovial joints.That contain a fluid called sinovial fluid inside a capsule and that’s why they are called cavitated joints.
1:Fibrous joints:-
These joints are made up of fibers.They don’t permit movement but some of them permit slight movement.These are classified into:
a)Sutures:
These are found in skull and are immoveable.
b)Syndesmosis:
when the bones are connected with interosseous ligament such joint is called sydesmosis.Such as inferior tibiofibular joints.
c)Gomphosis:
Peg and socket joints are called gomphosis joints.Example of this type of joint is root of the tooth in bony socket.
2:Cartilaginous joints:
When the articulating bones are joined by cartilage, such joint is called cartilagenous joint.These joints are of two types:
a)Primary cartilaginous joints:
These joints are immovable and the bones are united by hyaline cartilage.They are temporary and are replaced by bone in certain age.Example is joint between diaphysis and epiphysis in a long bone.
Primary cartilaginous joints are also called Synchondrosis.
b)Secondary cartilaginous joints:
In these joints the articulating surfaces are covered a thin layer of hyaline cartilage and then bones are united by disc of fibrocartillage. The joints are permanent in nature and permit limited movement.These are found mostly in the mid-line of the body such as inter-vertebral joints.
Secondary cartilaginous joints are also called Symphyses or fibrocartilaginous joints.
B)Cavitated joints:
It inculudes sinovial joints.
3:Synovial joints:
These joints help in the movements of different body parts and are the most mobile joints in the body because they have cavities in which bones move.They have sinovial membrane in which a lubricating fluid called sinovial fluid is present.
These are the different classification of joints but if you want to learn one or write on in exam then the most important one is structural classification.
Leave a Reply